(New York Jewish Week) — Shortly after the State of Israel was founded, Shanit Keter-Schwartz was born on a dirt floor, in a hut made of aluminum siding outside the burgeoning town of Tel Aviv. She was the second of six children, the daughter of Yemenite Jews who had recently immigrated to the new country. They’d faced discrimination and violence in their country of origin, so when Jewish emissaries turned up in 1949 to bring 50,000 Yemenite Jews to Israel as a part of “Operation Flying Carpet,” they were all in.
Unfortunately, Keter-Schwartz’s upbringing in Israel was no magic carpet ride. “[Yemenite Jews] were seen as savages, primitive, inferior in the eyes of the Ashkenazi Jews,” Keter-Schwartz recalled in an interview with the New York Jewish Week. “They were not sophisticated or educated. It was a cultural domination, a collective trauma in Israel. They faced war, hunger, poverty, and living in very harsh conditions.”
The worst, though, wasn’t near-starvation due to rationing, or the harsh conditions of the shanty towns that these new immigrants were placed in, or the way European children wrinkled their nose at her and called her smelly. No, the worst was when the government stole her sister, Sarah, whom Keter-Schwartz never saw again.
In what has become known as the Yemenite Children Affair, more than 1,000 children of Yemenite, Mizrahi and Balkan descent were separated from their families during the first decade of Israel’s existence. The families and their advocates have long insisted, over denials by officials, that the children were taken from their families by the Ashkenazi government during the first decade of Israel’s existence. More often than not, parents were told their children had died when they had, in fact, been given to families of European descent for adoption, according to Amram Association, one of several organizations dedicated to documenting these abductions and advocating for victims’ families.
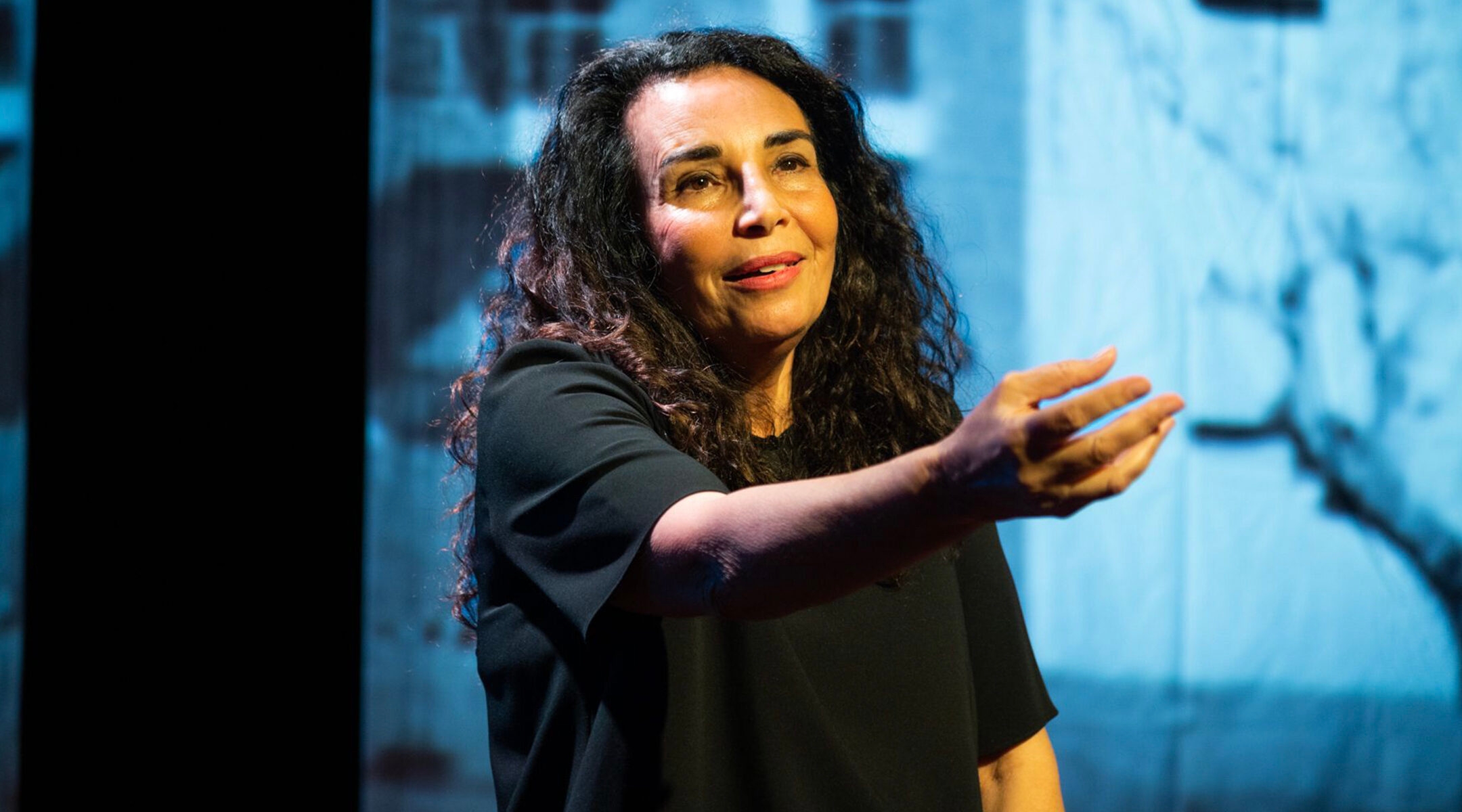
Now, Keter-Schwartz — a writer and performer who lives in Los Angeles, and a mother to two grown daughters — has brought to life her family’s story and her search for her missing sister in the form of a one-woman show. Premiering on Thursday at New York City Center, and running through May 15, “Daughter of the Wicked” chronicles her family’s journey from the Yemenite ma’abarot (refugee camps) to shikunim (government housing projects), where they lived in a tiny two-room apartment amid a melting pot of Jewish immigrants who were often at odds with one another.
“It is overcrowded, and the people who live here come from many different places. In their countries they were… respected by their communities,” she says in the show, which is named after one of the many Yemenite curses her mother would hurl at her when she’d done something wrong. “But here [in Israel] they are forced into stereotypes.”
“Israel had no choice but to bring the Jews from the Arab countries because the European Jews population had been greatly diminished after the Holocaust, but they didn’t want us,” Keter-Schwartz told the New York Jewish Week. “They took control of our lives, tried to assimilate us, wanted the whole country to be secular and uniform. They made all the decisions for us.”
One such “decision” made by the government, she said, was to remove her oldest brother, Yossi, from the family home to “re-educate” him at an Ashkenazi kibbutz. It worked: Yossi returned as a proud secular farmer, disdainful and ashamed of his spiritualist, religious family and their traditional ways.

The disappearance of her baby sister, Sarah, inspired Keter-Schwartz’s play, which is also informed by the kabbalistic teachings of her father. (Russ Rowland)
In the case of Keter-Schwartz’s sister, the abduction occurred directly after she was born. “When my father went to the hospital to pick up the twins, my siblings, he returned only with David. They told him that the girl, Sarah, was sick, and he should come back the following day. But when he came back, they told him that she had died,” Keter-Schwartz said. “Being naive, he didn’t question this. He didn’t ask to see a death certificate. He didn’t even know [a certificate] existed. He didn’t demand to see her body, didn’t think to bury her or give her funeral rites. He never suspected for a minute they could deceive him.”
This story, and others, is conveyed in “Daughter of the Wicked” through a series of monologues, each tied to an idea from Kabbalah,the Jewish mystical tradition. Keter-Schwartz defines each concept — like ahava (love), metsuka (hardship), busha (shame) — then tells a personal story that relates to the topic.
With this framework, Keter-Schwartz pays homage to her father, a spiritualist rabbi who spent his days poring over holy texts and divining the true meaning of the universe. She reads from his writings — which were collected and published towards the end of his life as a book, “Nachash HaNechoshet” — detailing her complex relationship to a man who was both an inspiration and, at times, inscrutable to all around him.
“The play is set in a hotel room, while I’m waiting for my sister to show up,” Keter-Schwartz explains. “As I wait, I tell my life. Behind me, on three screens, there’s archival footage from the 1950s that I got from Steven Spielberg’s archive. That footage tells the story, too, and so does the music.” The accompanying music, which transitions the audience from segment to segment, was written by Israeli composer Lilo Fedida, using traditional Yemenite melodies and instruments.
“We lived with this [tragedy] all my childhood, and I’ve been wondering all these years about my missing sister,” said Keter-Schwartz. “If I see her on the street, will I recognize her? Where does she live? Is she happy? I felt guilty that I never really tried to find her, I was so busy with my own life. But now I need to know.”
As a young woman, Keter-Schwartz said she went to great lengths to distance herself from her family’s tragedies. She lived in Amsterdam, London and New York, finally finding her footing in Los Angeles. She changed her name — from Shoshana to Shanit — and declared herself a new person in a new land. It was only when she lost all but one of her siblings, as well as both parents, that she felt an urge to revisit the past. When her last surviving sibling got so ill he almost died, she swore to search for Sarah. Initially, the idea was just to hire a private investigator to try to locate her. During her search, though, she began to feel an urge to share her story.
“I’d never written a play, so it took me two years [working] with coaches,” says Keter-Schwartz. “I’ve been an actress all my life, I’ve edited other people’s scripts, I produced movies, but to actually write — ha! I had amazing coaches. I’m especially grateful to Yigal Chatzor, the Israeli playwright. He brought the Israeli spice and the humor, which is wonderful now because now the play is balanced. It’s heart-wrenching and it’s hysterical. It’s everything, you know.”
The Yemenite Children Affair has never been formally confirmed by the state of Israel, which maintains the position that most of the babies died of malaria or malnutrition and were not, as some have proposed, sold to Ashkenazi families in exchange for donations to the young country. Several government-led commissions have claimed that there was no official wrongdoing, but testimonies continue to emerge that suggest otherwise. According to a 2016 article in Yediot Ahronot, a prominent Israeli news source, the government has sealed the official records of these disappearances until 2071, despite ongoing demonstrations and demands for actions.
In 2021, the Israeli government authorized tens of millions of dollars in reparations to families whose children disappeared while in government care. Nonetheless, no official admission of guilt or apology has been issued, a fact which caused many affected families to reject the plan, calling it “hush money.” Only a fraction of the affected families are eligible for these payments and, according to recent reporting, very few have claimed the money. Less than 1% of the allocated funds have been distributed thus far.
For Keter-Schwartz, no amount of money could compensate for the loss of her sister. She’s more interested in creating connections with others who lost family members and bringing awareness to this chapter in Israeli history. “Going back to my roots, revisiting the past, is an act of forgiveness,” Keter-Schwartz said in a statement. “By writing this play, I was able to forgive and accept the past. I hope that when audiences see my play they come to terms with their own history, and that they feel a sense of what it means to be free, and the challenges that confront us in maintaining that freedom.”
That is a major throughline of “Daughter of the Wicked”: Keter-Schwartz does not forsake the country that gave her her identity and childhood; rather, she insists on loving it while demanding recognition of past wrongs. Towards the end of her show, Keter Ashkenazi raises both arms to the sky and screams at those who wronged her: “My country! I blame you, shame on you for forsaking us, shame on you!”
But then, she lowers her arms and says, voice cracking with heartbreak: “I love you, I blame you, I love you. My country, I love you.”
The New York Jewish Week brings you the stories behind the headlines, keeping you connected to Jewish life in New York. Help sustain the reporting you trust by donating today.